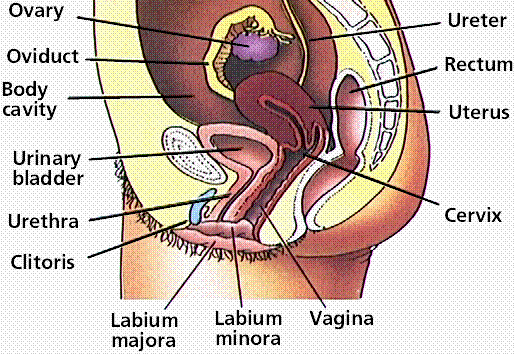
In the last post discussed the male reproductive organs. In this lesson let us gain some understanding of the working of the female reproductive organs that are totally different from the male organs.
The female reproductive organ includes the
external genital organs (vagina and clitoris), the cervix, the uterus, the
ovaries and the fallopian tubes.
The vagina is the muscular passage that
connects the cervix with the external organs. The clitoris is a small sensitive
part of tissue, which becomes larger when the female is sexually excited. The
cervix is the narrow lower part of the uterus where it joins the vagina. The
uterus (also called womb) is hollow, muscular structure in which a baby is
carried and nourished while it develop before birth. The ovaries are the two
glands that produce certain hormones and contain tissue sacks in which female
egg cells are produced and developed. The fallopian tubes are two muscular
channels that connect the ovaries to the uterus. The two finger-like projection
(called fimbriae) located at the opening of the fallopian tubes move an egg
releases from an ovary into the relevant fallopian tube.
Both the male and female reproductive
systems do not works continuously from birth onwards in the same way as the
other body systems such as the digestive system and the respiratory system
work. The reproductive system does not start to function until the age of
puberty. When this happens, the secondary sexual characteristics can be seen
all around the body. In addition, females indicate this more evidently because
of the menstruation process of their reproductive system.
Generally, for females, puberty takes place
between 8 and 5 years of the age, and the menopause takes place between 45 and
55 years. During this period the female reproductive system normally goes
through a series of regular changes, which is called the menstrual cycle. This
cycle normally lasts about 28 days and then repeats, though there is some
variation from one woman to another.
During the first part of the cycle, the
building up of the lining (tissue covering the inner surface) of the uterus (womb)
takes place. This is to provide a suitable environment to accept a fertilized
egg. Then, if the egg is not fertilized, this tissue starts to break down. When
the lining of the womb is got rid of, it result in a flow of blood and tissue
through vagina. This phase of the cycle, which last about 5-4 days, is called
menstruation. Counting from the first day of bleeding, an egg is normally
released about 14 (in the middle of the cycle). However, there can be some
variation, and the cycle length may also vary.
 As far as the reproductive organs are
concerned, women can make more use of certain simple yoga posture in order to easily
keep these organs free of various health imbalances. This is because unlike
men, women have all of their important reproductive organs inside their body.
So exercising these embedded organs in a soft way is very important for their
sound health.
As far as the reproductive organs are
concerned, women can make more use of certain simple yoga posture in order to easily
keep these organs free of various health imbalances. This is because unlike
men, women have all of their important reproductive organs inside their body.
So exercising these embedded organs in a soft way is very important for their
sound health.